Written by Katrina Heinze, OFRF Board Member from 2014-2023
A planned gift is a gift to the future. I support organic farming and OFRF because I care about the future health of our planet and its people. A planned gift to OFRF is a tangible way for me to pay it forward.
 My mom fed me organic milk before “organic” was even a label. I grew up cooking and connecting with people through food. Later in my career, these interests led me to work in organic foods and organic policy. What a gift! Through my work, I learned about the care, hard work, and amazing knowledge that organic farmers bring to growing our food, as well as the challenges that make farming organically and bringing a farm’s goods to market difficult.
My mom fed me organic milk before “organic” was even a label. I grew up cooking and connecting with people through food. Later in my career, these interests led me to work in organic foods and organic policy. What a gift! Through my work, I learned about the care, hard work, and amazing knowledge that organic farmers bring to growing our food, as well as the challenges that make farming organically and bringing a farm’s goods to market difficult.
In 2014, I joined OFRF’s board. Our farmer board members and farmer listening sessions taught me that organic farmers are experimenters and that we still have much to learn about the best production practices to nurture our environment, deal with and address the impacts of climate change, and provide healthy food for all—all while ensuring sustainable economics for farmers and farming communities.
OFRF’s mission is to foster the improvement and widespread adoption of organic farming systems. I love OFRF’s farmer-centered, science-based approach. Our work is long-term and requires long-term funding. For example, OFRF publishes the National Organic Research Agenda (NORA) every 5-6 years. The NORA Report is used to ask for Congressional funding for organic research, influence USDA’s grant funding, and help those of us in the organic food industry rally to support our farmers’ most important production (and non-production) needs. All of this contributes to new knowledge and support for organic farmers.
My husband and I have included OFRF in our will in addition to our regular OFRF donations. We did this to model our values for our family, demonstrate how we align our resources to those values, and be clear about the legacy we want to leave behind.
 Estate planning can be easy to put off or avoid. However, we found that having conversations with our family about our wishes enriched our relationships. By discussing what mattered most to us and how we could best use our resources now and in the future, we’ve become better stewards of our resources today. We are glad we did this now instead of waiting or missing the opportunity altogether.
Estate planning can be easy to put off or avoid. However, we found that having conversations with our family about our wishes enriched our relationships. By discussing what mattered most to us and how we could best use our resources now and in the future, we’ve become better stewards of our resources today. We are glad we did this now instead of waiting or missing the opportunity altogether.
Planned giving can take place during your lifetime or at death, and it is a crucial part of your overall financial and estate plan. Typically larger than donations from ordinary income, planned gifts can provide income, financial security, and tax savings to you and your family, depending on how they are structured. In our case, our planned gift includes a multi-year commitment to OFRF now and a designation of a percentage of any remaining estate at our deaths.
Planned giving is crucial for non-profits like OFRF, who depend largely on annual giving to “keep the lights on.” Although OFRF receives grants for key program initiatives, these grants don’t often pay for staff development, accounting, and the time-consuming work of helping policymakers understand the needs of farmers. Planned gifts build year-to-year stability for now and create a “savings account” for later.
I have seen the impact of planned gifts on OFRF. When I was on the Board of Directors, we received a planned gift. This single donation enabled us to hire a paid intern to support our research program. It also demonstrated to a future grant maker the value of our work, which has now resulted in a multi-year grant. Better still, the donor was unknown to us, and learning about why OFRF was important to them brought us joy and a renewed commitment to our mission.
A planned gift does not have to be complicated. Including OFRF as a beneficiary in your will or naming OFRF as a full or partial beneficiary of a life insurance policy or retirement account is a simple way to make a planned gift. Consulting with your financial and legal advisors can help you determine what is best for your situation and values. Once you have put a gift plan in place, let the beneficiary non-profit know. They will benefit from understanding what motivated you, and you will get to enjoy the impact of your thoughtful gift.
Together, let’s ensure the widespread adoption of organic farming practices. Our earth and farming communities depend on it. Please join me in planting a seed for the future by making a planned gift to OFRF today.
Sincerely,
Katrina





 The plot layout includes 12 accessions from a western regional station, all of Ethiopian origin, alongside two commercially available varieties:
The plot layout includes 12 accessions from a western regional station, all of Ethiopian origin, alongside two commercially available varieties: 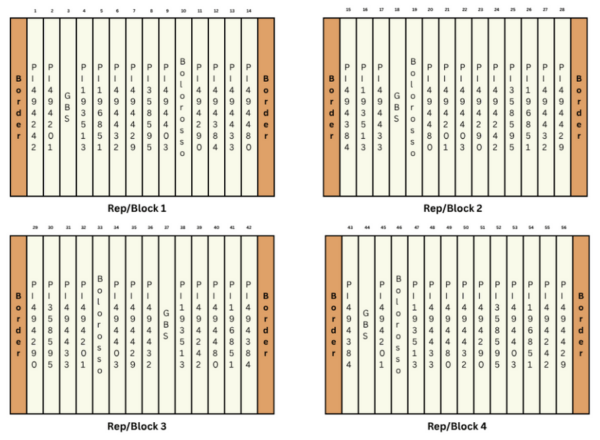








 My mom fed me organic milk before “organic” was even a label. I grew up cooking and connecting with people through food. Later in my career, these interests led me to work in organic foods and organic policy. What a gift! Through my work, I learned about the care, hard work, and amazing knowledge that organic farmers bring to growing our food, as well as the challenges that make farming organically and bringing a farm’s goods to market difficult.
My mom fed me organic milk before “organic” was even a label. I grew up cooking and connecting with people through food. Later in my career, these interests led me to work in organic foods and organic policy. What a gift! Through my work, I learned about the care, hard work, and amazing knowledge that organic farmers bring to growing our food, as well as the challenges that make farming organically and bringing a farm’s goods to market difficult.  Estate planning can be easy to put off or avoid. However, we found that having conversations with our family about our wishes
Estate planning can be easy to put off or avoid. However, we found that having conversations with our family about our wishes 

 Farmacea’s project is a strawberry trial comparing traditional plastic mulch to a living mulch of white Dutch clover. Their research question is simple but will help Farmacea determine which
Farmacea’s project is a strawberry trial comparing traditional plastic mulch to a living mulch of white Dutch clover. Their research question is simple but will help Farmacea determine which