Real Talk on EQIP: One Organic Farm’s Journey Through Federal Funding
The Story of Three Feathers Farm
(Versión en español a continuación / Spanish version below)
By Jazea Kalea Smith, OFRF Fall 2024 Policy and Communications Intern, and OFRF staff
OFRF is currently working to increase farmer and community awareness of the federal funding opportunities available to organic and transitioning farms. As part of our work with the West/Southwest region of the USDA’s Transition to Organic Partnership Program (TOPP), we’re spotlighting the experience of one farm—Three Feathers Farm in California—that received funding and support through the Natural Resource Conservation Service’s Environmental Quality Incentives Program (EQIP).
Their story offers a transparent look at what it’s really like to work with NRCS: the benefits, the obstacles, and the lessons they’ve learned. We hope other farmers can use their experience to navigate the process of applying for and implementing EQIP contracts more easily.
Meet Three Feathers Farm
 Three Feathers Farm is a small, BIPOC-led organic farm located on four-and-a-half acres in Morgan Hill, California, a mere twenty minutes south of San Jose, on the ancestral lands of the Muwekma Ohlone Tribe.
Three Feathers Farm is a small, BIPOC-led organic farm located on four-and-a-half acres in Morgan Hill, California, a mere twenty minutes south of San Jose, on the ancestral lands of the Muwekma Ohlone Tribe.
Founded by Héktor Calderón-Victoria and Dilip Sharma in 2022, the farm grows a mix of modern and traditional culturally relevant crops such as corn, pepper, beans, squash, onions, lettuce, radishes, tomatoes, flowers, culinary herbs, basil, and cucumbers. Their mission is to steward the land while providing food that serves and reflects the diverse communities that came before, and the ones that surround them now.
“I think for us, farming is not just a place for growing food, but a place where community comes together,” says Héktor. “It’s where people can bring different mindsets and lifestyles and economic backgrounds. Our mission is that we want to be able to be as diverse as our soil and our crops that we grow.”
In 2023, after a year of preparation—cleaning, designing, sourcing necessary farming equipment, studying the needs of the soil, the climate, pest pressure, and diseases, and prepping the site for practices such as cover cropping and composting—Three Feathers Farm officially began production. They quickly worked to establish relationships with local restaurants, non-profits, food banks, and even their local school district, an uncommon success for a new, small-scale operation.
From the start, they knew they would need funding to implement sustainable practices that aligned with their values. They found EQIP through their local Resource Conservation District office, which helped point them to the USDA’s Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS).
Working With NRCS and Putting Conservation Into Practice
 So far, Three Feathers Farm has received two NRCS-EQIP contracts. The first, awarded in 2023, was for a hedgerow border along the farm’s property line, which has been completed. The second, approved in 2024, supports the construction and maintenance of two high tunnels.
So far, Three Feathers Farm has received two NRCS-EQIP contracts. The first, awarded in 2023, was for a hedgerow border along the farm’s property line, which has been completed. The second, approved in 2024, supports the construction and maintenance of two high tunnels.
Getting to those signed contracts, however, took time, persistence, and a steep learning curve. The process began with a farm visit from a local NRCS field agent, followed by the creation of a conservation plan—a prerequisite for applying. Next came a series of forms, eligibility checks, and application submissions, including registering with the Farm Services Agency (FSA) to obtain a farm number, which Héktor, as a new farm owner, hadn’t realized was required.
“That was the biggest obstacle for us was—trying to understand what side of the USDA you go to for certain things, where you submit different paperwork, who to talk to. It felt like the two offices (FSA and NRCS) weren’t in communication with each other,” he explained.
Despite this complication, Three Feathers pushed forward, ultimately securing contracts for two impactful conservation projects:
Hedgerows for Biodiversity
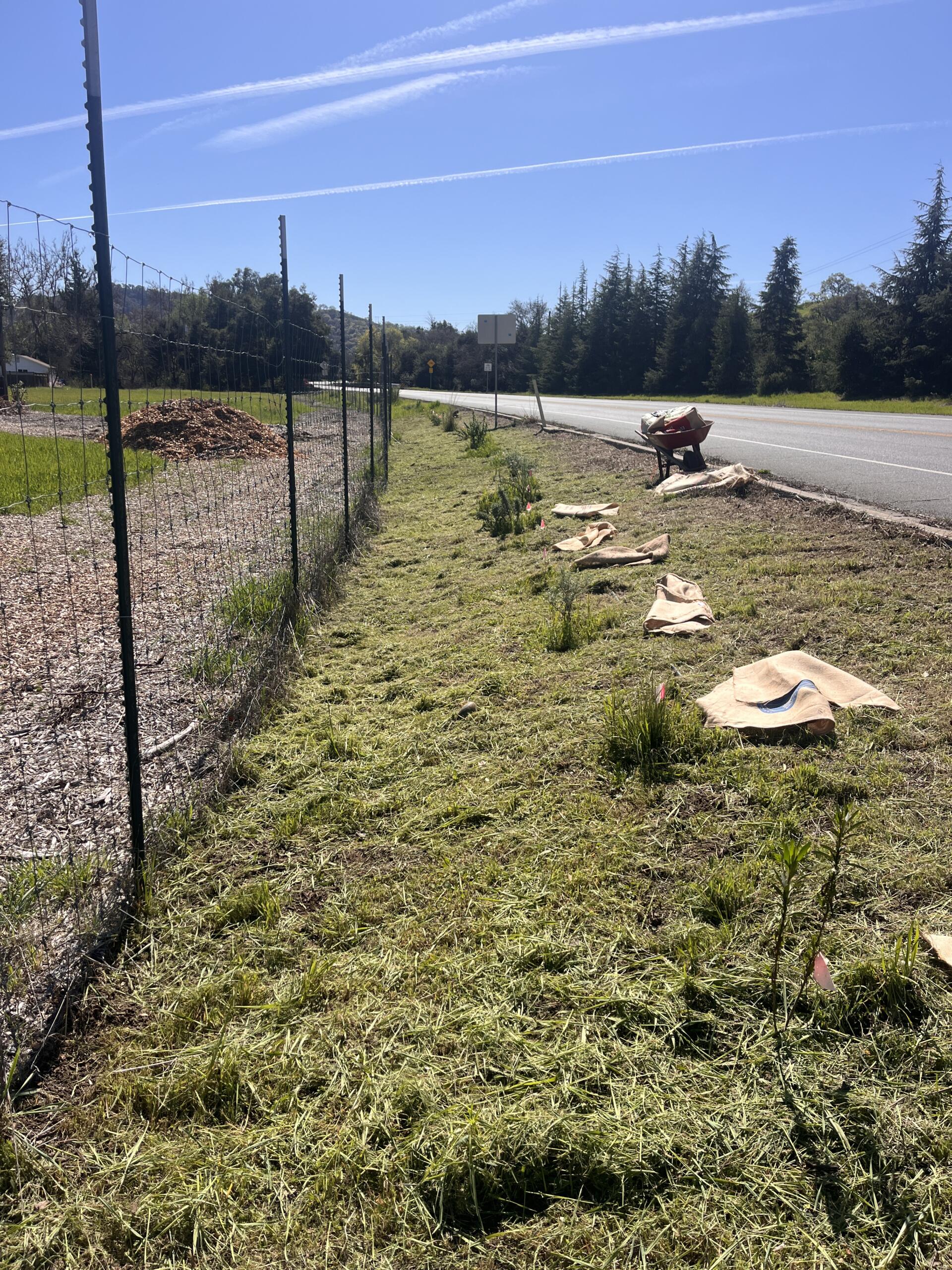
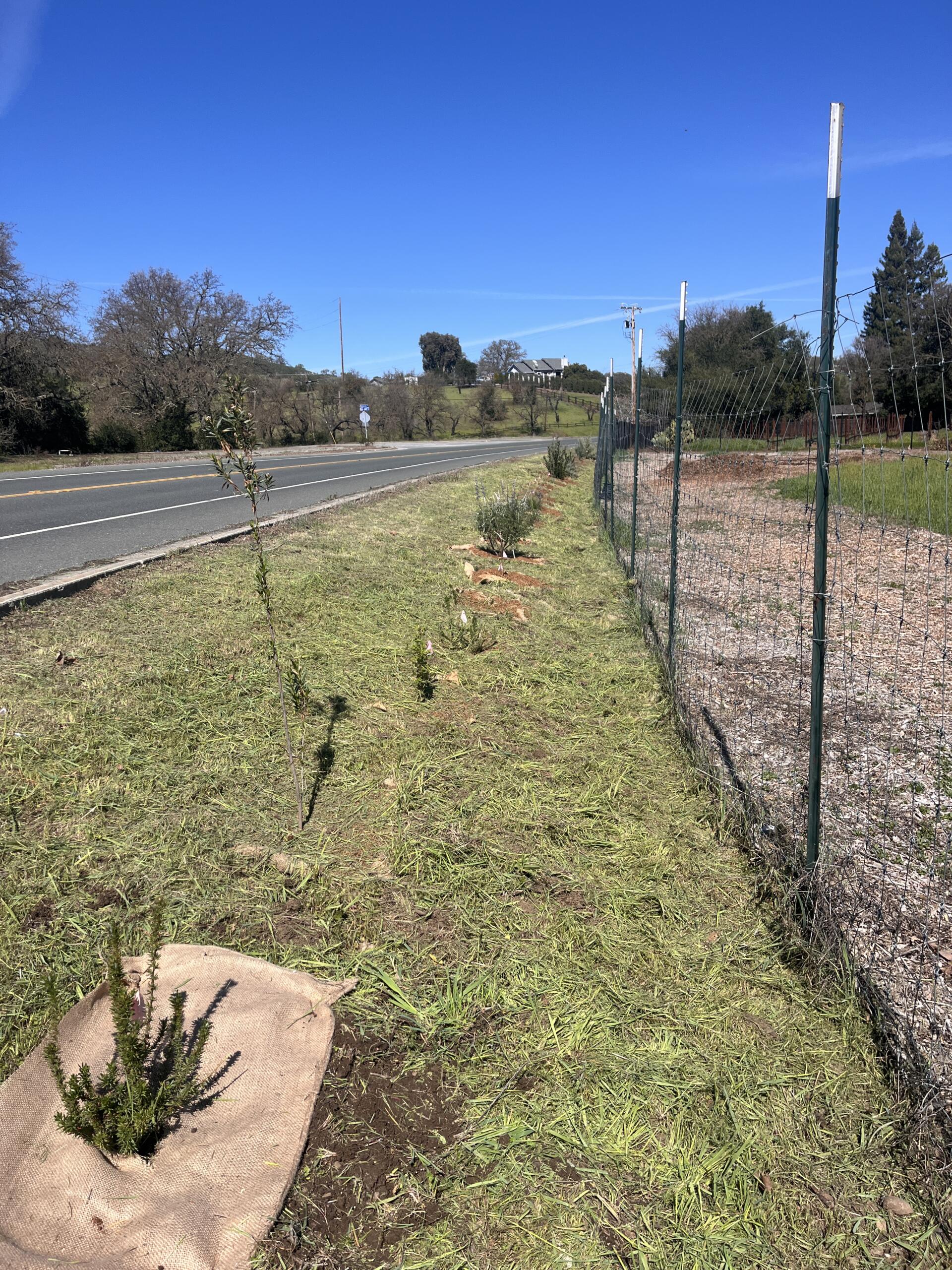
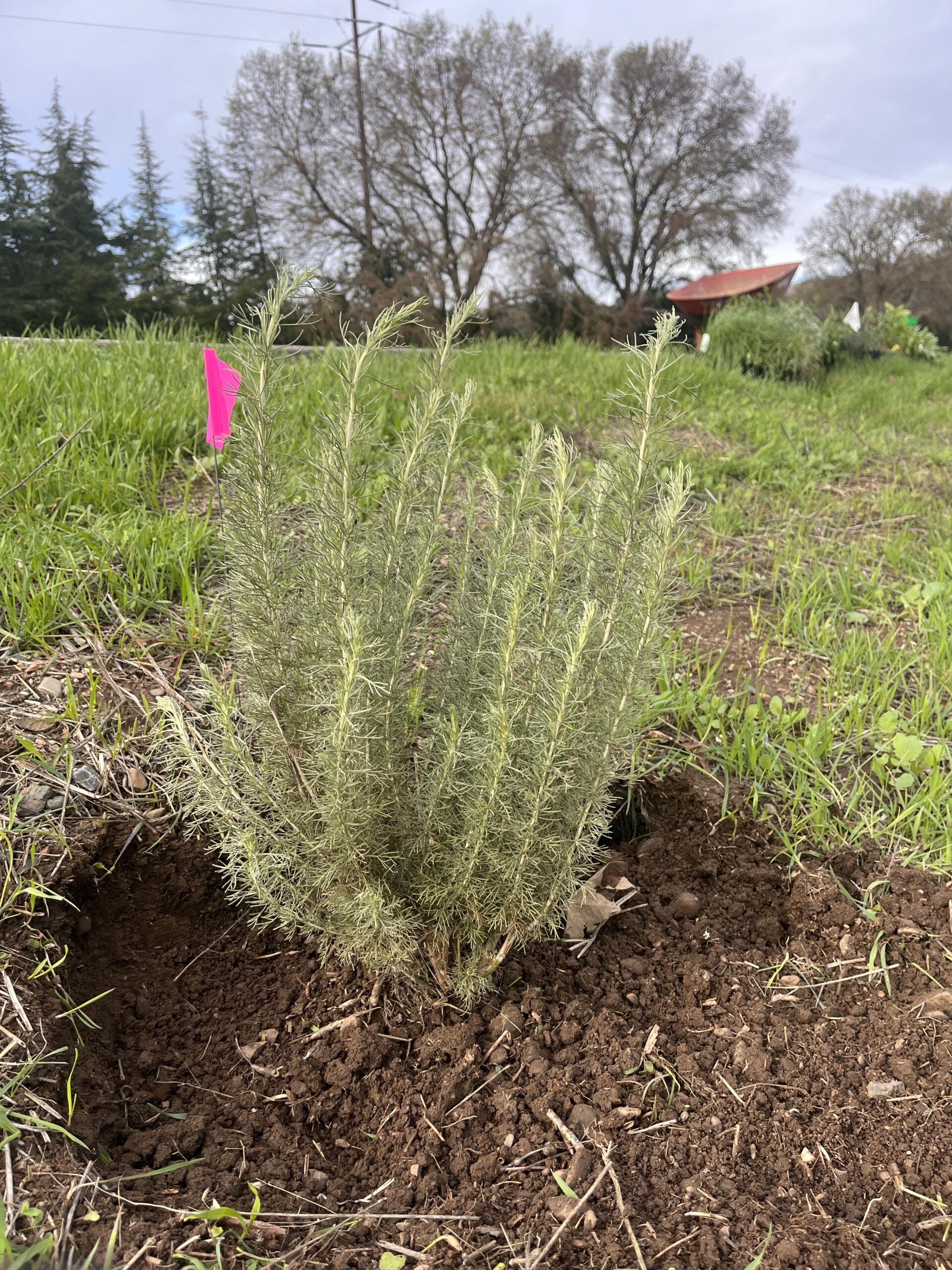
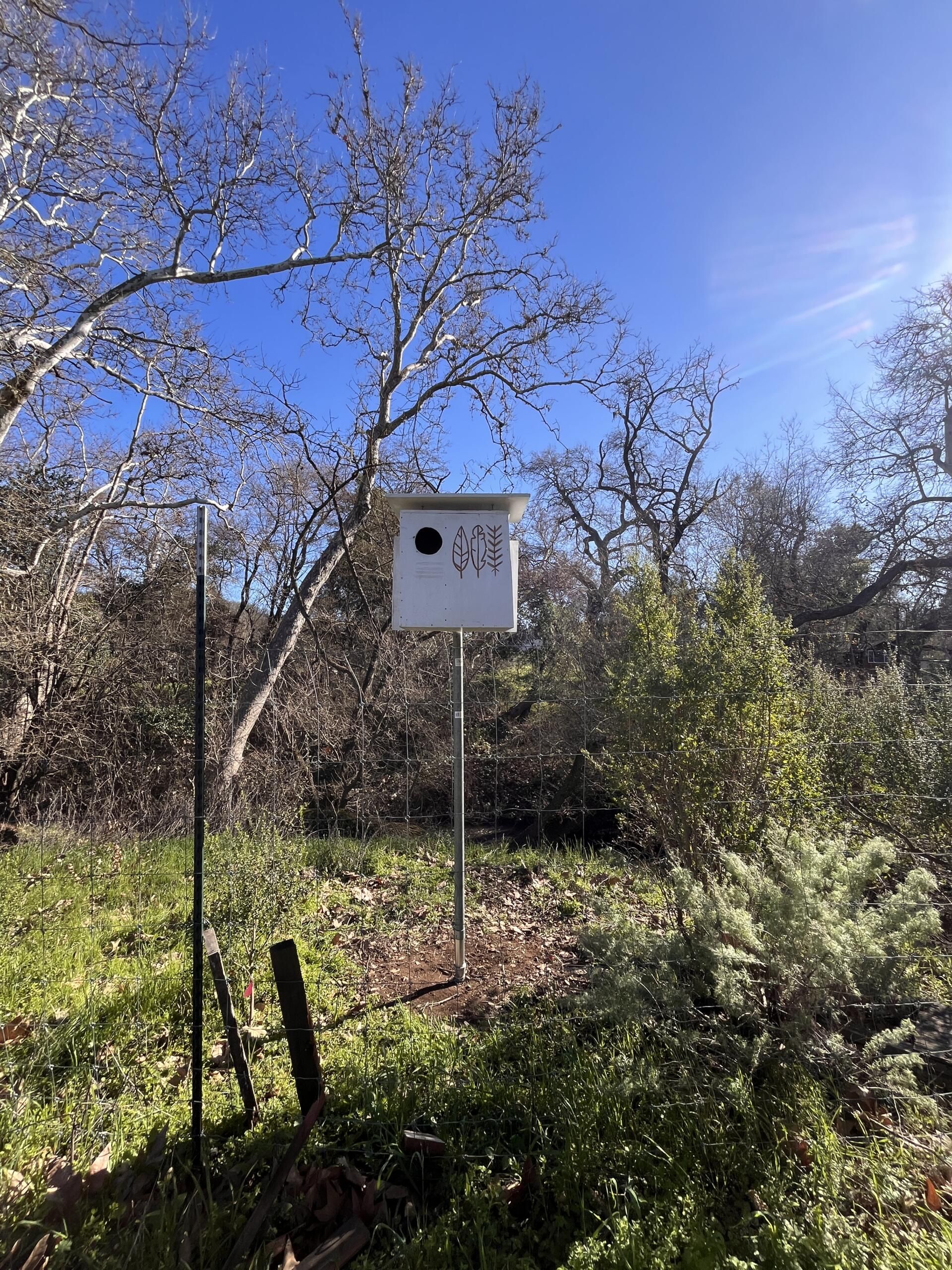
The hedgerow project funded the planting of a variety of native species along a border fence, helping prevent erosion, attract beneficial insects, and buffer wind. It also supported the construction of a barn owl nest box to naturally manage rodent pressure from squirrels and field mice. Maintenance, like regular irrigation and mulching, is required as part of the contract’s ongoing terms.
Prior to the stewardship action taken by Héktor and Dilip, no conservation practices had been applied at the Three Feathers Farm site. “We know this project will improve our water quality, reduce erosion for where the hedgerows will be, and increase biodiversity of the site that we have, by bringing beneficial insects and birds,” Héktor stresses.
High Tunnel Hurdles When Funding Doesn’t Flow Fast
The high tunnel contract, approved in late 2024, was designed to support two season-extending structures, with supplemental guidance on soil management like mulching and cover cropping under the tunnels. The high tunnels would allow the farm to grow sensitive crops through cooler months, protect against late frosts and intense rain events, and increase income stability through longer harvest periods.
But by March 2025, six months after the contract was signed, construction had not begun.
The main reasons: funding logistics and uncertainty. EQIP contracts typically reimburse farmers only after projects are completed and verified by a field agent, often several months or a year after costs have been incurred for project materials or contracted labor. Three Feathers Farm would need to front around $50,000 to complete the high tunnel installation before receiving any reimbursement. This can provide a financial challenge, especially for small farms who may not have access to a bunch of capital to front the cost of a conservation project.
“We’re not just big bags of money,” Héktor laughed. Often the solution for some farmers is to pull out an FSA loan or CDFI loan, but this takes a lot of time and effort and isn’t necessarily feasible for all farmers.
Compounding the issue was the timeline and lack of transparency in the process. Although their contract was approved in September 2024, they were still unclear when reimbursement would be available, which documents were required, and whether any updates had been processed six months later.
“Something that I had a really hard time with is that there is no centralized platform where all of the documents live to show what has been submitted, what contracts do we have, and when these contracts are done,” Héktor said.
They later learned that they could have applied for advance payment as a Historically Underserved operation—a USDA designation that can allow farmers to receive partial funding earlier. This option is still a reimbursement, but farmers are able to submit their receipts immediately after the expense is incurred, rather than having to wait until project completion. Covering expenses for a few weeks instead of several months or a year can make a huge difference in the financial viability of a project for a small farm.
However, Héktor expressed frustration that the option for advance payment was not disclosed to them at the time when they submitted their application. They only learned later that they could have been eligible for the advance payment option. At that point changing the application would have required restarting the whole process, creating a major setback to their project timeline.
“If we had it would have been a very different story,” said Héktor.
In the meantime, the farm is still working to identify financing options or partners to help them move forward with the project.
EQIP Lessons and Hurdles
While Héktor was quick to confirm that “these programs have been incredibly beneficial to our farm” he also pointed out some challenges that they experienced in working with the USDA. These challenges offer valuable lessons for other farmers interested in participating in federal support programs, and also give insight to improvements that NRCS agencies could implement in the processes used and staff training provided.
Navigating FSA and NRCS Requirements
Héktor emphasized that one of the earliest hurdles was not knowing that registering with FSA and obtaining a farm identification number was required before applying for NRCS programs like EQIP. For beginning farmers, this step—and the need to navigate two separate USDA entities—isn’t always intuitive.
The USDA is a large and complex organism with many different agencies working within it. This “doesn’t make it easy for small scale producers to navigate and to understand the complexities of the US government program,” Héktor explained
Language Matters
Despite participating in two different EQIP projects, Héktor pointed out that he and his business partner weren’t clear on exactly which Conservation Practice Standards (CPS) their projects actually supported. CPSs are methods that the NRCS has found to address Resource Concerns.. These technical terms tend to be second nature to NRCS agents, but can leave farmers in the dark.
It would be helpful, Héktor suggested, if NRCS agents were better equipped to speak in terms that are familiar to farmers, helping them understand the connection between their farming practices and the conservation goals of the agency. That way “when we are talking to our elected officials or talking to other organizations we can actually tell them what we’re doing as part of these contracts,” Héktor said.
Communication Gaps and Outdated Systems
Héktor cited communication and use of technology as one of the major challenges that Three Feathers Farm experienced throughout the process of working with a USDA contract.
“The application for both FSA and NRCS felt very archaic,” Héktor said. They were “relying on methods and platforms that weren’t user-friendly or conducive to effectively being able to submit and track documents. It just felt like there’s got to be an easier way.”
This led to a lot of uncertainty about what paperwork needed to be submitted and whether everything required had been properly received by NRCS. It was difficult for Three Feathers Farm to know if they were missing any key documents or steps, Héktor explained, “which added to the stress of the application process, for both me and my business partner.”
“Despite these challenges, we worked diligently to navigate the system by carefully double-checking and following up on each of the steps,” Héktor said, a key tip for other farmers applying for these programs.
Long Delays and Understaffing
“We experienced huge wait times, sometimes 2-4 months, to schedule even just a visit from our field agent,” Héktor explained. “This delay had a significant impact on our ability to move forward with submitting our applications for programs we wanted to apply to–like hedgerows and high tunnels.”
While he stressed that their local field agent was helpful and supportive, it was clear that understaffing limits how quickly farmers can move forward. “They probably have so many farmers they have to respond to that it’s not possible for them to give us the attention that we need,” he added.
For Three Feathers Farm, this made it hard to get a response and meant that they had to constantly be reaching out to their NRCS office to push the project along and make sure things were on track.
Agent Awareness of Practices that Apply to Organic Farms
Héktor expressed a desire for more familiarity on the part of NRCS agents with the programs that could work on an organic farm, pointing out how helpful it would be if they were more able to suggest practices for farmers to consider implementing that are compatible with the organic method.
“We found that agents were not always fully aware of the practices and programs that could apply to our farm,” Héktor mentioned. “I think as a result we sometimes miss out on new or existing programs that could be beneficial to our operation.”
Because of this, Héktor pointed out the importance for farmers to be proactive in asking for support, and doing the work of familiarizing themselves with the programs that are available.
Project Timelines and Reimbursements
Three Feathers Farm was approved for their high tunnel project in September 2024, but by early March 2025, they still hadn’t been able to break ground. Delays—both in scheduling and in understanding the materials sent as part of the contract—have slowed the process. The timeline from application to implementation to reimbursement can be longer and more complex than expected, especially for new applicants who may not anticipate these challenges or factor them into their planning.
While an Advance Payment option exists to help eligible farmers get reimbursed sooner, it wasn’t offered upfront.
Don’t wait until you’re ready to build. Ask detailed questions about timelines and whether you qualify for Advance Payment.
Advice to Others
Despite the challenges, Héktor wants other farmers to know the programs are worth it—if you’re ready to do some extra legwork.
“It taught us that we needed to be really persistent, to pay attention to the details, and to advocate for ourselves,” he said. “Don’t be afraid to ask questions, and don’t assume the agencies will volunteer all the information you need. You have to advocate for it.”
Héktor acknowledges that these programs have eliminated the significant long-term financial burden from incorporating these practices onto Three Feathers Farm, “enabling us to now invest in our sustainable practices without jeopardizing our farm’s [financial] sustainability. The guidance and technical assistance that we’ve received have really streamlined our processes, contributing to our broader goal of environmental stewardship.”
Looking Ahead: Stewardship, Research, and Resilience
Three Feathers Farm became USDA Certified Organic in early 2024, but Héktor and Dilip’s long-term vision goes beyond infrastructure or certification. They see organic farming as part of a broader movement rooted in environmental stewardship, food justice, and cultural resilience.
“We’re in continual kinship with the soil, crops that we grow, and the surrounding nature in our area,” Héktor said.
For Three Feathers Farm, organic isn’t just a label—it’s a responsibility to their community and future generations. That includes advocating for better research, more accessible programs, and a stronger voice for small farms in federal conversations.
Héktor has traveled to Washington, D.C. as an advocate with the National Young Farmers Coalition and continues to speak out about the importance of policy that reflects the lived experiences of diverse farmers. He highlighted the lack of research on culturally relevant crops and the needs for greater recognition of Traditional Ecological Knowledge (TEK) in agricultural research.
“A lot of the crops we grow don’t have data behind them for pest and disease management,” he explained. “That forces small farms like ours to do our own research, which takes time we don’t always have.”
Preservation is a common thread in their motivations to go organic, culminating in the greater goal of protecting the land for future generations. Both human and animal communities benefit from land free of chemical pesticides and herbicides, and the choice to receive organic certification is largely about providing accountability. Three Feathers Farm wants its community to know that they “did their due diligence,” and feel that the organic label communicates that.
Although achieving certification was an arduous process, the technical support and monetary backing of a number of organizations and agencies played a large role in enabling the farm to reach this goal. One critical factor that sped up their application timeline was the fact that previous farming operations on that plot had ceased more than twenty years before, meaning that the three-year transition period for land rehabilitation was unnecessary—a requirement Héktor noted can deter some farmers with fewer resources.
OFRF continues to advocate for more research funding that centers BIPOC producers, and to develop resources to help all farmers access the support they need to thrive. As climate change accelerates and challenges deepen, farms like Three Feathers remind us what’s at stake–and what’s possible when farmers have the right tools.
Ready to Apply? Here Are a Few Helpful Resources
If you’re a farmer considering applying for EQIP or other NRCS programs, here are some helpful tools to get started:
- Download a printable summary of the key takeaways for farmers to consider when applying to NRCS EQIP here.
- Download OFRF’s EQIP flyer for more information on the federal funding program, including eligibility and application details, available in English and Spanish here.
- Connect with your local NRCS office to start developing a conservation plan: nrcs.usda.gov/contact
- Know your eligibility. Farmers who are classified as beginning, limited-resource, socially disadvantaged, or veterans may qualify for higher reimbursement rates and advance payments.
- Ask about the advance payment option early. This can be a game-changer for small farms with limited cash flow.
Hablemos en serio sobre EQIP: El recorrido de una granja orgánica a través de los fondos federales
La historia de Three Feathers Farm
Por Jazea Kalea Smith, pasante de Políticas y Comunicaciones de OFRF en otoño de 2024, y el personal de OFRF
En OFRF, actualmente estamos trabajando para aumentar el conocimiento entre agricultores y comunidades sobre las oportunidades de financiamiento federal disponibles para granjas orgánicas y en transición. Como parte de nuestro trabajo con la región Oeste/Suroeste del Programa de Asociación para la Transición a la Producción Orgánica (TOPP) del USDA, queremos destacar la experiencia de una granja: Three Feathers Farm, en California, que recibió fondos y apoyo a través del Programa de Incentivos a la Calidad Ambiental (EQIP, por sus siglas en inglés) del Servicio de Conservación de Recursos Naturales (NRCS).
Su historia ofrece una mirada honesta a lo que realmente implica trabajar con el NRCS: los beneficios, obstáculos y lecciones aprendidas. Esperamos que otras granjas puedan usar esta experiencia para navegar el proceso de solicitud e implementación de contratos de EQIP.
Conozca a Three Feathers Farm
 Three Feathers Farm es una pequeña granja orgánica dirigida por personas BIPOC, ubicada en cuatro acres y medio en Morgan Hill, California, a solo veinte minutos al sur de San José, en tierras ancestrales de la Tribu Muwekma Ohlone.
Three Feathers Farm es una pequeña granja orgánica dirigida por personas BIPOC, ubicada en cuatro acres y medio en Morgan Hill, California, a solo veinte minutos al sur de San José, en tierras ancestrales de la Tribu Muwekma Ohlone.
Fundada por Héktor Calderón-Victoria y Dilip Sharma en 2022, la granja cultiva una combinación de cultivos modernos y tradicionales con relevancia cultural, como maíz, chile, frijoles, calabazas, cebolla, lechuga, rábanos, jitomates, flores, hierbas culinarias, albahaca y pepinos. Su misión es cuidar la tierra mientras ofrecen alimentos que sirvan y reflejen a las diversas comunidades que los antecedieron y que los rodean actualmente.
“Yo creo que para nosotros, la agricultura no es solo un lugar para cultivar alimentos, sino un espacio donde la comunidad se reúne”, dice Héktor. “Es un sitio donde las personas pueden traer distintas formas de pensar, estilos de vida y trasfondos económicos. Nuestra misión es ser tan diversos como lo son nuestro suelo y los cultivos que cultivamos”.
En 2023, después de un año de preparación—limpiar el terreno, diseñar, conseguir el equipo agrícola necesario, estudiar las necesidades del suelo, el clima, las plagas y enfermedades, y preparar el sitio para prácticas como cultivos de cobertura y compostaje—Three Feathers Farm comenzó oficialmente su producción. Rápidamente establecieron relaciones con restaurantes locales, organizaciones sin fines de lucro, bancos de alimentos e incluso con su distrito escolar local, lo cual es un logro poco común para una operación nueva de pequeña escala.
Desde el principio, sabían que necesitarían financiamiento para implementar prácticas sostenibles que coincidieran con sus valores. Descubrieron EQIP a través de su oficina local del Distrito de Conservación de Recursos, que los orientó hacia el Servicio de Conservación de Recursos Naturales (NRCS) del USDA.
Trabajar Con el NRCS y Poner la Conservación En Práctica
 Hasta ahora, Three Feathers Farm ha recibido dos contratos EQIP del NRCS. El primero, otorgado en 2023, fue para una cerca viva a lo largo del límite de la propiedad, la cual ya ha sido completada. El segundo, aprobado en 2024, apoya la construcción y mantenimiento de dos túneles altos.
Hasta ahora, Three Feathers Farm ha recibido dos contratos EQIP del NRCS. El primero, otorgado en 2023, fue para una cerca viva a lo largo del límite de la propiedad, la cual ya ha sido completada. El segundo, aprobado en 2024, apoya la construcción y mantenimiento de dos túneles altos.
Sin embargo, llegar a esos contratos firmados tomó tiempo, persistencia y una proceso de aprendizaje difícil. El proceso comenzó con una visita de campo por parte de un agente local del NRCS, seguida de la creación de un plan de conservación—un requisito previo para la solicitud. Luego vino una serie de formularios, verificación de elegibilidad y presentación de solicitudes, incluyendo el registro en la Agencia de Servicios Agrícolas (FSA) para obtener un número de granja, algo que Héktor, como nuevo propietario de una granja, no sabía que era necesario.
“El mayor obstáculo para nosotros fue tratar de entender a qué parte del USDA acudir para ciertas cosas, dónde entregar distintos formularios, con quién hablar. Sentíamos que las dos oficinas (FSA y NRCS) no se comunicaban entre sí”, explicó.
A pesar de esta complicación, Three Feathers siguió adelante, y finalmente logró asegurar contratos para dos proyectos de conservación con gran impacto:
Cercas vivas para la biodiversidad
El proyecto de cercas vivas financió la siembra de una variedad de especies nativas a lo largo de una cerca perimetral, ayudando a prevenir la erosión, atraer insectos beneficiosos y amortiguar el viento. También incluyó la construcción de una caja nido para lechuzas como forma natural de controlar roedores, como ardillas y ratones de campo. Como parte de los términos del contrato, se requiere mantenimiento continuo, como riego regular y acolchado.
Antes de que Héktor y Dilip implementaran estas prácticas de manejo, no se había aplicado ninguna práctica de conservación en Three Feathers Farm. “Sabemos que este proyecto mejorará la calidad del agua, reducirá la erosión en el área donde estará la cerca viva, y aumentará la biodiversidad del sitio que tenemos, al atraer insectos y aves beneficiosas”, enfatiza Héktor.
Obstáculos en Túneles altos cuando el financiamiento no llega rápido
El contrato para los túneles altos, aprobado a fines de 2024, fue diseñado para apoyar la construcción de dos estructuras que extienden la temporada de cultivo, con orientación complementaria sobre el manejo del suelo, como el acolchado (“mulching”) y el cultivo de cobertura (“cover cropping”) dentro de los túneles. Estos túneles permitirían a la granja cultivar cultivos sensibles durante los meses más fríos, protegerlos de heladas tardías y lluvias intensas, y aumentar la estabilidad de ingresos mediante periodos de cosecha más largos.
Pero en marzo de 2025, seis meses después de firmar el contrato, la construcción aún no había comenzado.
Las principales razones: logística financiera e incertidumbre. Los contratos EQIP normalmente reembolsan a los agricultores solo después de que los proyectos se completan y un agente de campo los verifica, lo que a menudo ocurre varios meses o incluso un año después de que se hayan incurrido los costos de materiales o mano de obra contratada. Three Feathers Farm necesitaba desembolsar alrededor de $50,000 para completar la instalación antes de recibir algún reembolso. Esto puede representar un desafío financiero, especialmente para granjas pequeñas que quizás no cuenten con capital suficiente para cubrir los costos por adelantado.
“No somos sacos grandes de dinero”, se rió Héktor. A menudo, la solución para algunos agricultores es recurrir a un préstamo de FSA o de una Institución Financiera de Desarrollo Comunitario (CDFI, por sus siglas en inglés), pero esto requiere mucho tiempo y esfuerzo, y no siempre es factible para todos.
El problema se agravó con los plazos y la falta de transparencia en el proceso. Aunque su contrato fue aprobado en septiembre de 2024, seis meses después todavía no tenían claro cuándo estaría disponible el reembolso, qué documentos se requerían y si se habían procesado actualizaciones seis meses después.
“Algo que me costó mucho fue que no hay una plataforma centralizada donde estén todos los documentos, que muestre qué se ha enviado, qué contratos tenemos y cuándo están finalizados esos contratos”, dijo Héktor.
Más adelante se enteraron de que podían haber solicitado un pago adelantado por ser una operación designada como “Históricamente Desatendida”—una categoría del USDA que permite a los agricultores recibir una parte de la financiación más pronto. Esta opción sigue siendo un reembolso, pero los agricultores pueden presentar sus recibos inmediatamente después de incurrir en los gastos, en lugar de tener que esperar hasta la finalización del proyecto. Cubrir los gastos por unas semanas en lugar de varios meses o un año puede hacer una gran diferencia para la viabilidad financiera de un proyecto en una granja pequeña.
Sin embargo, Héktor expresó su frustración porque esa opción de pago adelantado no se les presentó cuando enviaron su solicitud. Solo más adelante supieron que podían haber sido elegibles. Para entonces, cambiar la solicitud habría requerido reiniciar todo el proceso, lo que habría representado un gran retraso para su cronograma.
“Si lo hubiéramos hecho, habría sido una historia muy diferente”, dijo Héktor.
Mientras tanto, la granja sigue buscando opciones de financiamiento o socios que los ayuden a avanzar con el proyecto.
Lecciones y obstáculos con EQIP
Aunque Héktor rápidamente confirmó que “estos programas han sido increíblemente beneficiosos para nuestra granja”, también señaló varios desafíos que enfrentaron al trabajar con el USDA. Estas experiencias ofrecen lecciones valiosas para otros agricultores interesados en participar en programas federales de apoyo, y también resaltan áreas en las que NRCS podría mejorar sus procesos y la capacitación de su personal.
Navegando los requisitos de FSA y NRCS
Héktor enfatiza que uno de los primeros obstáculos fue no saber que debían registrarse con FSA y obtener un número de identificación agrícola antes de aplicar a programas NRCS como EQIP. Para agricultores principiantes, este paso—y la necesidad de navegar entre dos agencias diferentes del USDA—no siempre es intuitivo.
“USDA es un organismo grande y complejo con muchas agencias distintas trabajando dentro de él. Esto no facilita que los productores a pequeña escala entiendan y naveguen la complejidad de los programas del gobierno estadounidense”, explicó Héktor.
El lenguaje importa
Aunque participaron en dos proyectos diferentes de EQIP, Héktor señaló que ni él ni su socio comercial tenían claridad sobre cuáles “Estándares de Prácticas de Conservación” (CPS, por sus siglas en inglés) apoyaban realmente sus proyectos. Los CPS son métodos que NRCS ha determinado que abordan problemas de recursos. Estos términos técnicos son naturales para los agentes de NRCS, pero pueden dejar a los agricultores en la oscuridad.
Sería útil, sugirió Héktor, que los agentes de NRCS estén mejor capacitados para comunicarse en términos más comprensibles para los agricultores, ayudándoles a entender la conexión entre sus prácticas agrícolas y los objetivos de conservación de la agencia. Así, “cuando hablemos con funcionarios electos u otras organizaciones, podamos realmente explicar lo que estamos haciendo como parte de estos contratos”, dijo Héktor.
Brechas de comunicación y sistemas obsoletos
Héktor mencionó que uno de los principales desafíos que Three Feathers Farm experimentó fue la comunicación y el uso de tecnología a lo largo del proceso de trabajar con el contrato de USDA.
“La aplicación para FSA y NRCS nos pareció muy anticuada”, dijo Héktor. “Dependían de métodos y plataformas que no eran fáciles de usar ni ayudaban a enviar y rastrear documentos de forma efectiva. Sentíamos que debía haber una manera más sencilla”.
Esto causó mucha incertidumbre sobre qué documentos debían enviar y si NRCS había recibido todo correctamente. “No sabíamos si faltaban papeles importantes o pasos del proceso”, explicó Héktor, lo que aumentó el estrés tanto para él como para su socio.
“A pesar de estos desafíos, trabajamos con diligencia para navegar el sistema revisando cuidadosamente cada paso y haciendo seguimiento”, dijo Héktor un consejo clave para otros agricultores que estén considerando aplicar a estos programas.
Largos retrasos y falta de personal
“Experimentamos tiempos de espera muy largos, a veces de 2 a 4 meses, solo para agendar una visita de nuestro agente de campo”, explicó Héktor. “Este retraso tuvo un impacto significativo en nuestra capacidad de avanzar con la presentación de solicitudes para programas como las cercas vivas y los túneles altos”.
Si bien destacó que su agente local fue servicial y solidario, quedó claro que la falta de personal limita cuán rápido los agricultores pueden avanzar. “Seguramente tienen muchos agricultores a los que deben responder y no pueden darnos la atención que necesitamos”, añadió.
Para Three Feathers Farm, esto hizo que fuera difícil obtener respuestas y significó que debían estar en constante contacto con su oficina local de NRCS para impulsar el proyecto y asegurarse de que todo siguiera avanzando.
Conocimiento de prácticas aplicables a la agricultura orgánica
Héktor expresó su deseo de que los agentes de NRCS estén más familiarizados con los programas que pueden aplicarse a granjas orgánicas. Señaló lo útil que sería que los agentes pudieran sugerir prácticas compatibles con métodos orgánicos.
“Nos dimos cuenta de que los agentes no siempre estaban completamente informados sobre las prácticas y programas que podrían aplicarse a nuestra granja”, mencionó Héktor. “Creo que a veces eso hace que perdamos oportunidades en programas nuevos o ya existentes que podrían beneficiarnos”.
Por eso, resaltó la importancia de que los agricultores sean proactivos al pedir apoyo y se tomen el tiempo de familiarizarse con los programas disponibles.
Cronogramas de proyectos y reembolsos
Three Feathers Farm recibió la aprobación para su proyecto de túnel alto en septiembre de 2024, pero para principios de marzo de 2025, aún no habían podido comenzar la obra. Los retrasos, tanto en la programación como en la comprensión de los materiales incluidos en el contrato, hicieron más lento el proceso. El tiempo desde la solicitud hasta la implementación y el reembolso puede ser más largo y complejo de lo que se espera, especialmente para quienes participan por primera vez y no anticipan estos desafíos ni los incorporan en su planificación.
Aunque existe una opción de Pago por Adelantado para ayudar a que los agricultores elegibles reciban reembolsos más pronto, no se ofreció desde el inicio.
No espere hasta estar listo para construir. Haga preguntas detalladas sobre los cronogramas y si califica para el Pago por Adelantado.
Consejos para otras personas agricultoras
A pesar de los desafíos, Héktor quiere que otras personas agricultoras sepan que los programas valen la pena, siempre y cuando usted esté dispuesto a hacer un esfuerzo adicional.
“Nos enseñó que necesitábamos ser realmente persistentes, prestar atención a los detalles y abogar por nosotros mismos”, dijo. “No tenga miedo de hacer preguntas y no asuma que las agencias le proporcionarán toda la información que necesita. Usted debe abogar por obtenerla”.
Héktor reconoce que estos programas eliminaron una carga financiera significativa a largo plazo al incorporar estas prácticas en Three Feathers Farm, “lo que ahora nos permite invertir en nuestras prácticas sostenibles sin poner en riesgo la sostenibilidad [financiera] de nuestra granja. La orientación y asistencia técnica que hemos recibido realmente agilizaron nuestros procesos y contribuyeron a nuestro objetivo más amplio de cuidado ambiental”.
Mirando hacia el futuro: cuidado del entorno, investigación y resiliencia
Three Feathers Farm obtuvo la certificación orgánica del USDA a principios de 2024, pero la visión a largo plazo de Héktor y Dilip va más allá de la infraestructura o la certificación. Consideran la agricultura orgánica como parte de un movimiento más amplio, enraizado en el cuidado del medioambiente, la justicia alimentaria y la resiliencia cultural.
“Mantenemos un vínculo constante con el suelo, los cultivos que cultivamos y la naturaleza que nos rodea”, dijo Héktor.
Para Three Feathers Farm, ser orgánico no es solo una etiqueta: es una responsabilidad con su comunidad y con las futuras generaciones. Eso incluye abogar por una mejor investigación, programas más accesibles y una voz más fuerte para las granjas pequeñas en las conversaciones a nivel federal.
Héktor ha viajado a Washington, D.C. como defensor con la National Young Farmers Coalition, y continúa alzando la voz sobre la importancia de que las políticas reflejen las experiencias reales de agricultores diversos. Destacó la falta de investigación sobre cultivos culturalmente relevantes y la necesidad de un mayor reconocimiento del Conocimiento Ecológico Tradicional (TEK, por sus siglas en inglés) en la investigación agrícola.
“Muchos de los cultivos que cultivamos no cuentan con datos disponibles sobre el manejo de plagas y enfermedades”, explicó. “Eso obliga a granjas pequeñas como la nuestra a hacer su propia investigación, lo cual requiere tiempo que no siempre tenemos”.
La preservación es una motivación constante en su decisión de hacer la transición a lo orgánico, con el objetivo final de proteger la tierra para las generaciones futuras. Tanto las comunidades humanas como animales se benefician de un terreno libre de pesticidas y herbicidas químicos, y la decisión de obtener la certificación orgánica tiene mucho que ver con rendir cuentas. Three Feathers Farm quiere que su comunidad sepa que “hicieron las cosas bien” y sienten que la etiqueta orgánica comunica eso.
Aunque lograr la certificación fue un proceso arduo, el apoyo técnico y financiero de varias organizaciones y agencias desempeñó un papel fundamental para que la granja alcanzara esa meta. Un factor crítico que aceleró el cronograma de su solicitud fue el hecho de que las operaciones agrícolas anteriores en ese terreno habían cesado más de veinte años atrás, lo que significó que no fue necesario cumplir con el periodo de transición de tres años para la rehabilitación del suelo—un requisito que, según Héktor, puede desanimar a agricultores con menos recursos.
OFRF continúa abogando por más fondos de investigación que centrados a productores BIPOC, y para desarrollar recursos que ayuden a todas las personas agricultoras a acceder al apoyo que necesitan para prosperar. A medida que el cambio climático se acelera y los desafíos se profundizan, granjas como Three Feathers nos recuerdan lo que está en juego—y lo que es posible cuando las personas agricultoras tienen las herramientas adecuadas.
¿Listo/a para aplicar? Aquí tiene algunos recursos útiles
Si usted es una persona agricultora y está considerando solicitar EQIP u otros programas de NRCS, aquí tiene algunas herramientas útiles para comenzar:
- Descargue un resumen imprimible con los puntos clave que deben tener en cuenta las personas agricultoras al aplicar al EQIP de NRCS.
- Descargue el volante de EQIP de OFRF para obtener más información sobre este programa federal de financiación, incluidos detalles sobre elegibilidad y solicitud, disponible en inglés y español.
- Conéctese con su oficina local de NRCS para comenzar a desarrollar un plan de conservación: nrcs.usda.gov/contact
- Conozca su elegibilidad. Las personas agricultoras que se clasifican como principiantes, con recursos limitados, históricamente desatendidas o veteranas podrían calificar para tasas de reembolso más altas y pagos adelantados.
- Pregunte sobre la opción de pago adelantado desde el principio. Esto puede marcar una gran diferencia para granjas pequeñas con flujo de caja limitado.











 Up on a ridge in rural Maine is Kennebec Valley Farm, a 22-acre historic farm. Owner Jennifer Barrientos was able to purchase the farm three years ago to become steward of the property, which is a mix of woodland and pastureland. Jennifer grows on just about one acre, including greenhouses. She is certified organic and uses no-till and biodynamic methods to grow her produce. You’ll also find chickens and alpacas on her pastureland, and she makes good use of their manure in her soil fertility regimen.
Up on a ridge in rural Maine is Kennebec Valley Farm, a 22-acre historic farm. Owner Jennifer Barrientos was able to purchase the farm three years ago to become steward of the property, which is a mix of woodland and pastureland. Jennifer grows on just about one acre, including greenhouses. She is certified organic and uses no-till and biodynamic methods to grow her produce. You’ll also find chickens and alpacas on her pastureland, and she makes good use of their manure in her soil fertility regimen.  With technical support from OFRF, Jennifer built out her trial, asking, “Will purchased soil amendments result in higher yield and soil health when compared to farm-made compost in brassica crops?”
With technical support from OFRF, Jennifer built out her trial, asking, “Will purchased soil amendments result in higher yield and soil health when compared to farm-made compost in brassica crops?”















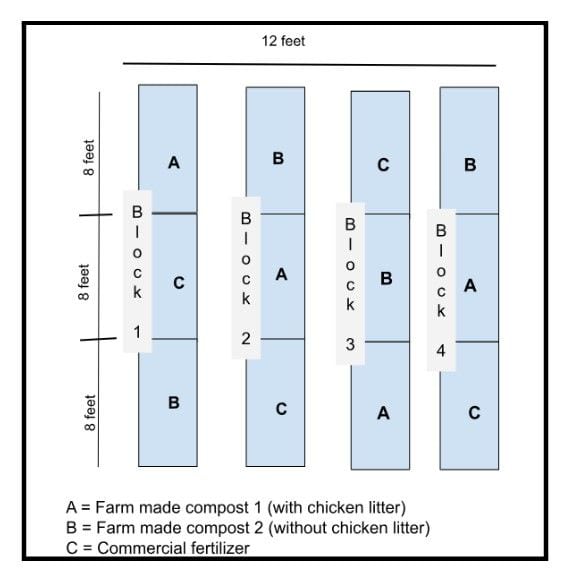













 To compare the moisture levels of the two treatments, Jorge purchased a soil moisture sensor. To date, he has conducted two measurements, one in late June and one in mid-July. Based on those readings, Jorge already sees a clear winner: The soil around the mulched grapevines has consistently been showing good moisture levels, while the readings around the un-mulched plants show dry conditions. Jorge’s own observations confirm this: “The mulch is like a double win, the mulch holds the moisture for longer and it suppresses the weeds as well… There are also a lot of creatures and biological activity in the mulched areas, while just putting the soil probe into the un-mulched areas was a challenge, as the soil was hard,” Jorge said.
To compare the moisture levels of the two treatments, Jorge purchased a soil moisture sensor. To date, he has conducted two measurements, one in late June and one in mid-July. Based on those readings, Jorge already sees a clear winner: The soil around the mulched grapevines has consistently been showing good moisture levels, while the readings around the un-mulched plants show dry conditions. Jorge’s own observations confirm this: “The mulch is like a double win, the mulch holds the moisture for longer and it suppresses the weeds as well… There are also a lot of creatures and biological activity in the mulched areas, while just putting the soil probe into the un-mulched areas was a challenge, as the soil was hard,” Jorge said.





 The average American family spends
The average American family spends