Reflections on Cover Crops and the Vital Role They Play in Organic Farming
By April Thatcher, farmer at April Joy Farm and OFRF Board President

Cover Crop Seed at AJF | Oats, radish, vetch, barley, and red clover.
Cover crops are a central part of balance on my Southwest Washington farm. In fact, they’re a vital tool in organic systems across the United States, helping to regenerate the soil, suppress weeds, and build resilience in the face of a changing climate. And yet, I’ll admit, for all their benefits, cover crops have been a source of some head-scratching moments for me over the years.
When I first started using cover crops, I had a lot of questions—many of the same ones I still hear from other new growers today.
- What mix of plants will work best with my soil type, climate, and crop needs?
- How do I know my cover crops are adding value to my system?
- What type of equipment do I need to manage cover crops successfully?
- And perhaps the most common question I get from fellow farmers is: How do I transition from a lush, green cover crop to a seedbed ready for planting without disturbing the soil too much?
Organic farming is a relationship between the land and the farmer, and I think of cover cropping as one big, ongoing conversation in this relationship. It’s a journey of experimentation, observation, learning, and refining techniques year after year. Each piece of land, each crop, and each season calls for a different approach, and what works for one farmer might not work for another.
On my farm, I’ve spent years experimenting with different cover crop mixes and timing strategies. I currently use a mix of cover crops—grasses, legumes, and broadleafs—depending on what I observe the soil needs. Legumes like peas and clover can add nitrogen to the soil, while deep-rooted crops like daikon radishes help break up compacted layers and improve soil structure. The key for me is to support functional diversity—both above and below the ground.
The Role of Cover Crops in a Living Soil System
When we treat soil as simply a medium to grow crops, we miss out on the extraordinary potential it has to regenerate life, sequester carbon, improve the nutritional value of our food, reduce off farm inputs, and to act as a buffer against the many challenges we face today.
Cover crops are a powerful tool to help unlock this potential. These crops are not meant to be harvested but rather are grown specifically to feed the soil. When used strategically, cover crops can help reduce soil erosion, capture and recycle nutrients, promote nitrogen fixation, increase organic matter, suppress weeds, and even manage pests—all while nurturing the living, complex web of life in our soils.
Cover crops are a critical tool in the organic farmer’s tool box to help build resilience on the ground—not just in the soil but in our entire farm ecosystem. And that resilience is more important now than ever as climate change presents erratic new challenges to farmers across the country.
Lessons from the Field: Cover Cropping in Practice
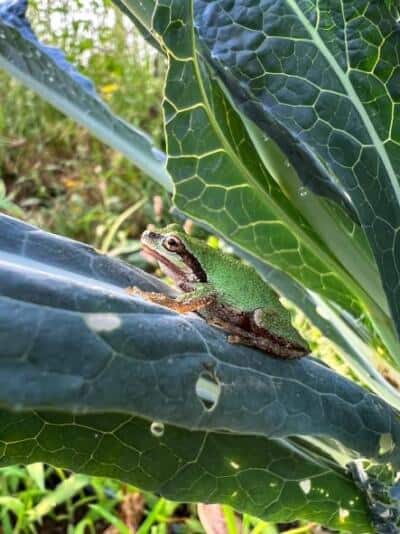

Cover Crop Kale | Sometimes, we don’t mow or turn under our market crops after we’ve finished harvesting. We underseed cover crops directly into these fields because, like cover crops, these plants continue to provide benefits for our system. Case in point- this tree frog has it made in the shade. Photo credit: Lauren Ruhe
I’ve learned over the years that there is no one “right” way to utilize cover crops. I’ve surrendered to the reality that on highly diversified operations like mine, cover cropping is always going to be a process of experimentation, observation, and refinement. What works one year might not work exactly the same the next, and that’s okay. If we are observant and committed to keeping records of our trials, we can glean important knowledge every season of the year. The goal isn’t perfection; it’s progress.
After eighteen years of working with cover crops on my 24 acre farm, here’s a bit of what I have gleaned – what I would tell my new-farmer-self if I could:
- Start simple and make small adjustments to your basic cover crop plan year over year. When I first started utilizing cover crops I was overly enthusiastic. Every year I’d try a bunch of different, complex seed mixes to try and find the perfect one. That was a mistake. I wish I’d stuck with a simple mix of two or three species (grass/legume/broadleaf) for the first few years. If I had done so, and made small refinements year over year, (adjust seeding rates, sowing dates, etc.) it would have saved me time in the long run. Instead of changing way too many variables every year, I would have built up a steady, reliable mix customized to my system faster- one that incrementally added stacking benefits to my system year over year.
- Pick only one (or two at most) goals. I had so many needs when I started using cover crops. I had soil compaction, low nitrogen, low organic matter levels, and erosion and leaching to worry about. But starting out, I would have been better off picking just one of these to focus on addressing through the use of cover crops instead of trying to solve all of them at once. Over time, you can build on your success. But aim for the small wins, having faith they will add up over time.
- Be mindful of your equipment and resource limits. We have hot, dry summers at my farm. So interestingly, irrigation is a big challenge for me in terms of using summer cover crop crops. Same goes for sowing fall cover crops, which I want to sow as early as I can to maximize nitrogen fixation. Even though I have the equipment to sow, cultipack and terminate them successfully, if I can’t get them to germinate without water I’m at square one. If you don’t have equipment to crimp/roll cover crops or don’t have a flail mower, make sure to be strategic about the species in your mix. Have a plan for seeding, and have a plan for terminating your cover crops that is practical for your operation.
- Nest your cover crops into your overall crop system. Your cover cropping plan has to work within the larger context of your farm plan. Part of this means being realistic about the resources (including labor) necessary to implement your cover crop strategy (see bullet point above). Part of this means being diligent about planning your cover cropping efforts as diligently as you do crops for your market. It’s all too easy in the heat of the season to bail on your cover cropping plan because some of the details aren’t quite worked out or you didn’t order seed, etc. Be intentional about making sure your cover crop system compliments versus competes with your market crop system. At my farm, tasks for cover crop soil prep, sowing, management, monitoring, and termination tasks are all included in my annual farm plan schedule. I don’t have to think about organizing or planning anything cover crop related once the season gets started; I can focus simply on implementation.
Every farmer who wishes to utilize cover crops successfully has specific soil health needs, goals unique to their operation, and different equipment and time constraints. So while there’s no single, universally right approach to cover cropping, we can all benefit from taking a strategic approach to working with cover crops.
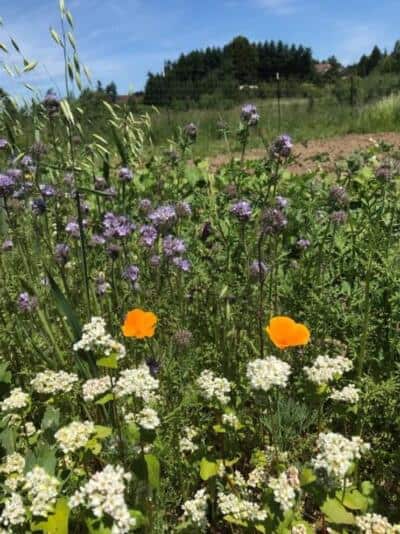

Summer Cover Crop Mix | A favorite combination for warm weather. Oats, Buckwheat, Poppies and Phacelia.
Bridging Experience with Research: OFRF’s New Guide to Cover Cropping
That’s why I’m so excited to share a valuable new resource for farmers: a comprehensive organic cover cropping guide developed through OFRF’s ongoing partnership with the Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS). This guide is designed to help farmers—whether they’re just starting out with cover crops or refining their strategies.
What makes this guide so valuable is that it’s grounded in both science and experience. It combines years of research on the benefits of cover cropping with practical, field-tested strategies from organic farmers like myself. It provides an overview of the steps for selecting cover crops, managing them through the growing season, and terminating them in a way that benefits both the soil and the farmer’s bottom line. And it offers a collection of other regionally specific resources for farmers to dive in deeper. You can also find more in depth information in OFRF’s Soil Health and Organic Farming guide to Cover Crop Selection and Management.
Whether you’re looking to improve your soil’s health, reduce off-farm inputs, support pollinators, or make your farm more resilient to climate change, cover crops can be a powerful tool in your toolkit. This guide is full of practical, research-based advice to help farmers make informed decisions about how to integrate cover crops into their systems.





 Samantha Otto is the founder and farmer of The Woven Trifecta, a 10-acre farm in western Michigan. Currently in transition to organic, the farm focuses on diversified vegetables for a CSA, local farmers market, as well as farm-to-school sales throughout the school year. Samantha raises Jacob sheep for fiber as well as assorted poultry for meat and eggs. The livestock is rotationally grazed on just over 3 acres of pasture, with 2 acres of no-till beds in production.
Samantha Otto is the founder and farmer of The Woven Trifecta, a 10-acre farm in western Michigan. Currently in transition to organic, the farm focuses on diversified vegetables for a CSA, local farmers market, as well as farm-to-school sales throughout the school year. Samantha raises Jacob sheep for fiber as well as assorted poultry for meat and eggs. The livestock is rotationally grazed on just over 3 acres of pasture, with 2 acres of no-till beds in production.
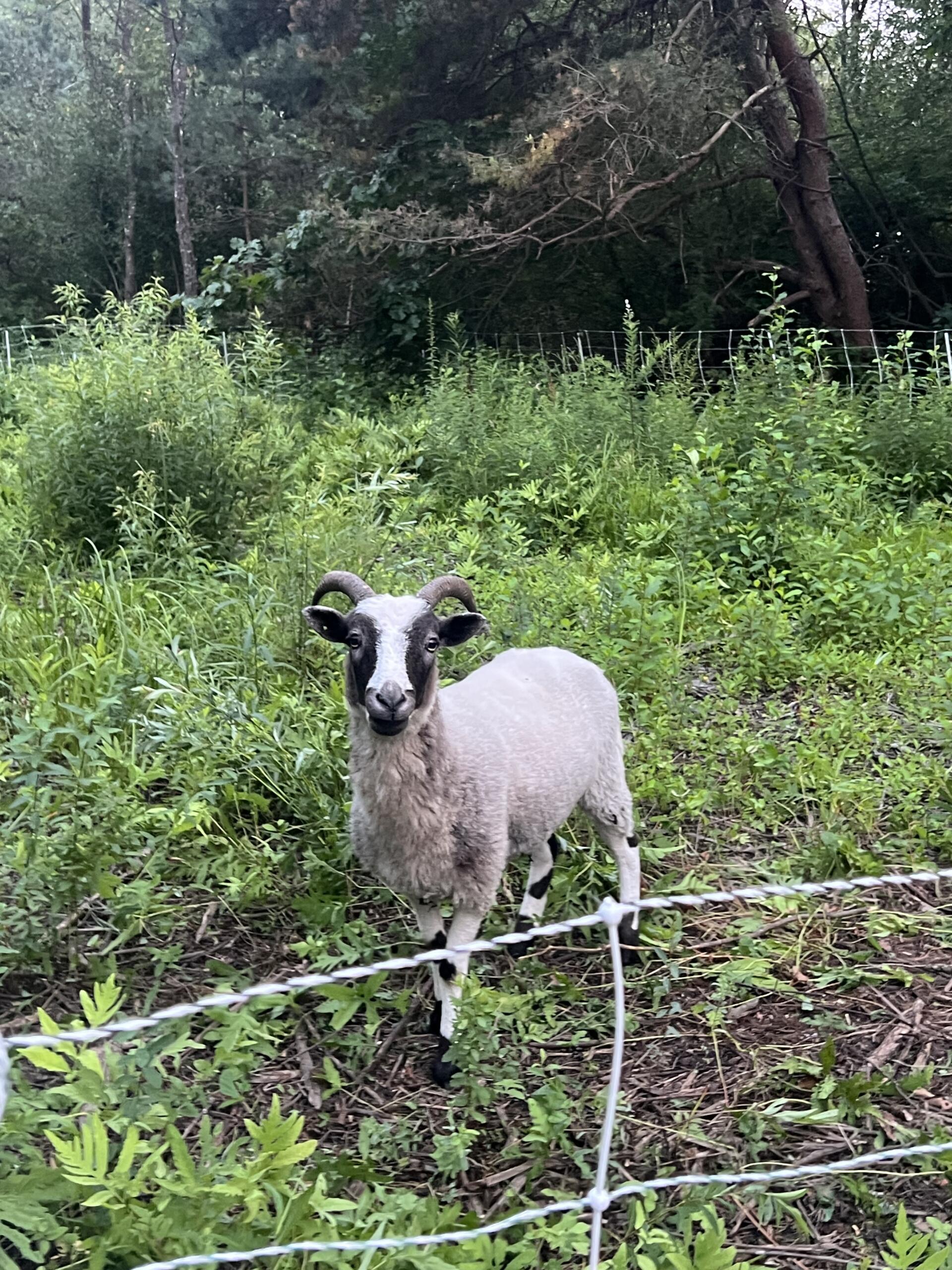







 Up on a ridge in rural Maine is Kennebec Valley Farm, a 22-acre historic farm. Owner Jennifer Barrientos was able to purchase the farm three years ago to become steward of the property, which is a mix of woodland and pastureland. Jennifer grows on just about one acre, including greenhouses. She is certified organic and uses no-till and biodynamic methods to grow her produce. You’ll also find chickens and alpacas on her pastureland, and she makes good use of their manure in her soil fertility regimen.
Up on a ridge in rural Maine is Kennebec Valley Farm, a 22-acre historic farm. Owner Jennifer Barrientos was able to purchase the farm three years ago to become steward of the property, which is a mix of woodland and pastureland. Jennifer grows on just about one acre, including greenhouses. She is certified organic and uses no-till and biodynamic methods to grow her produce. You’ll also find chickens and alpacas on her pastureland, and she makes good use of their manure in her soil fertility regimen.  With technical support from OFRF, Jennifer built out her trial, asking, “Will purchased soil amendments result in higher yield and soil health when compared to farm-made compost in brassica crops?”
With technical support from OFRF, Jennifer built out her trial, asking, “Will purchased soil amendments result in higher yield and soil health when compared to farm-made compost in brassica crops?”